As interest in cryptocurrencies continues to grow, more investment and trading options are available than ever before. While most people start out purchasing cryptocurrencies through a centralized exchange (CEX), as decentralized finance (DeFi) continues to grow, so do decentralized exchanges (DEXs). How do DEXes work?
The first decentralized exchange was created in 2014. Like everything else, it had to go through a long journey to become more accessible and easier to use. A DEX is a peer-to-peer marketplace where transactions occur directly between crypto traders. It works by using smart contracts to fulfill orders placed by traders, allowing users to trade directly with each other without a third party. Since DEXs do not involve any centralized parties, they are not subject to a regulatory inquiry. Users don't have to go through KYC (know your customer) or even open an account to trade.
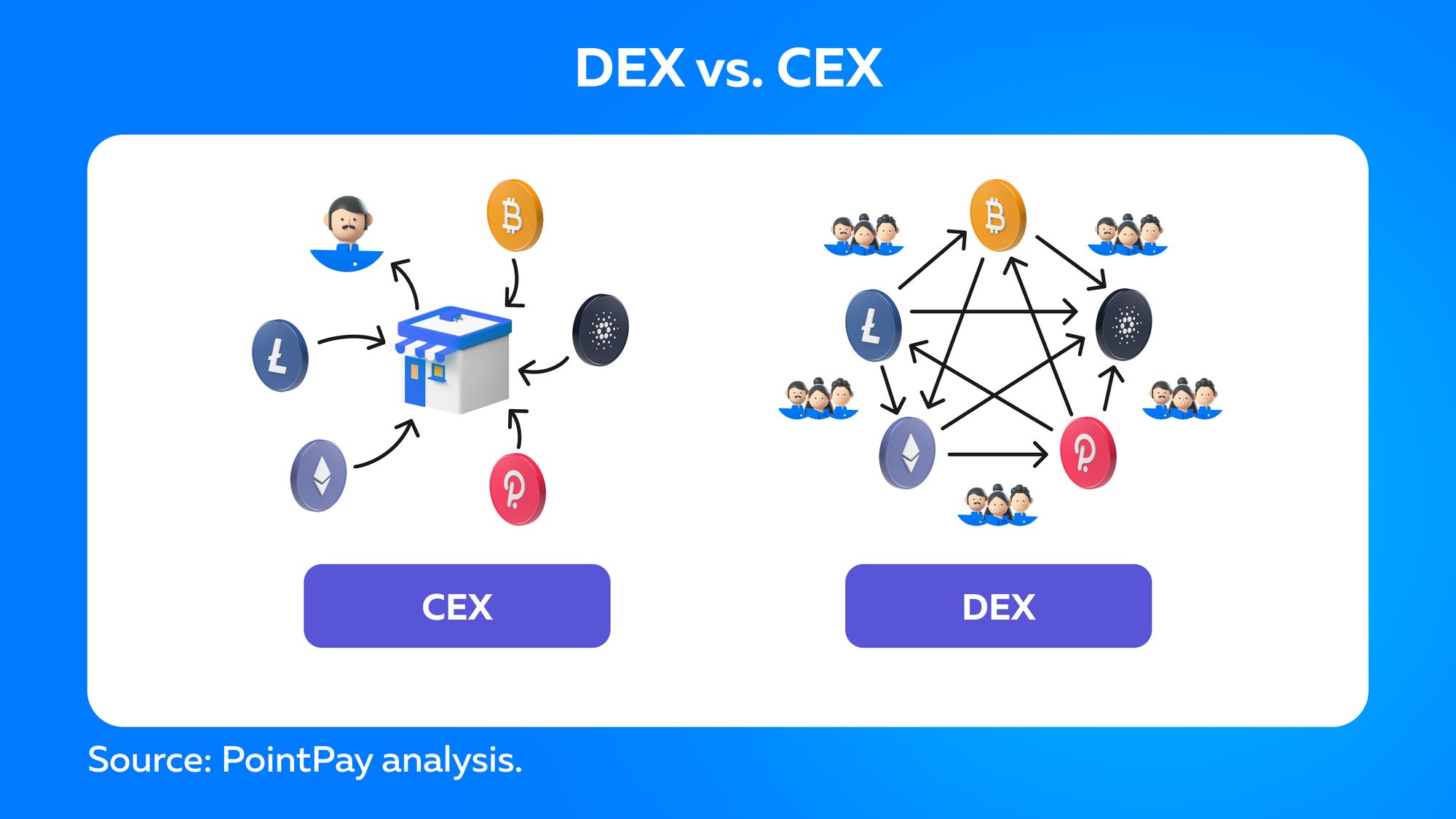
How do DEXs work?
The concept of decentralization is gaining popularity as traders look for ways to execute transactions without intermediaries. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are designed to remove the need for any authority to oversee and authorize trades performed within a particular exchange.
When traders use DEX, unlike CEX, their funds are not held on the exchange. Instead, users initiate trades directly, depositing cryptocurrency into their non-centralized wallets. The services offered by a CEX can be compared to those offered by a bank.
With a non-custodial wallet, you have complete control over your private keys, allowing you to manage your cryptocurrencies and provide ownership proof for any funds. A private key is a type of advanced encryption that enables users to access their cryptocurrencies. Users can easily access their crypto assets after logging into the DEX with their private key. They will not be required to enter any personal information like names and addresses. This is great for individuals who cherish their privacy.
A DEX uses smart contracts as its central authority. Unlike CEX, which uses middlemen to make trades on its platform, a DEX relies on smart contracts to fulfill the same role. Smart contracts are pieces of code that allow two people to enter into an agreement. We can say that they serve as legal agreements, but instead, they are written in code. If both parties do what they agree to, a smart contract will work as it should.
In the past, most DEXs used order books, a system that records all the open buy and sells orders placed on an exchange. While many DEXs still use order books today, more automation is available. This has made DEXs hugely popular due to their simplicity and increased liquidity!
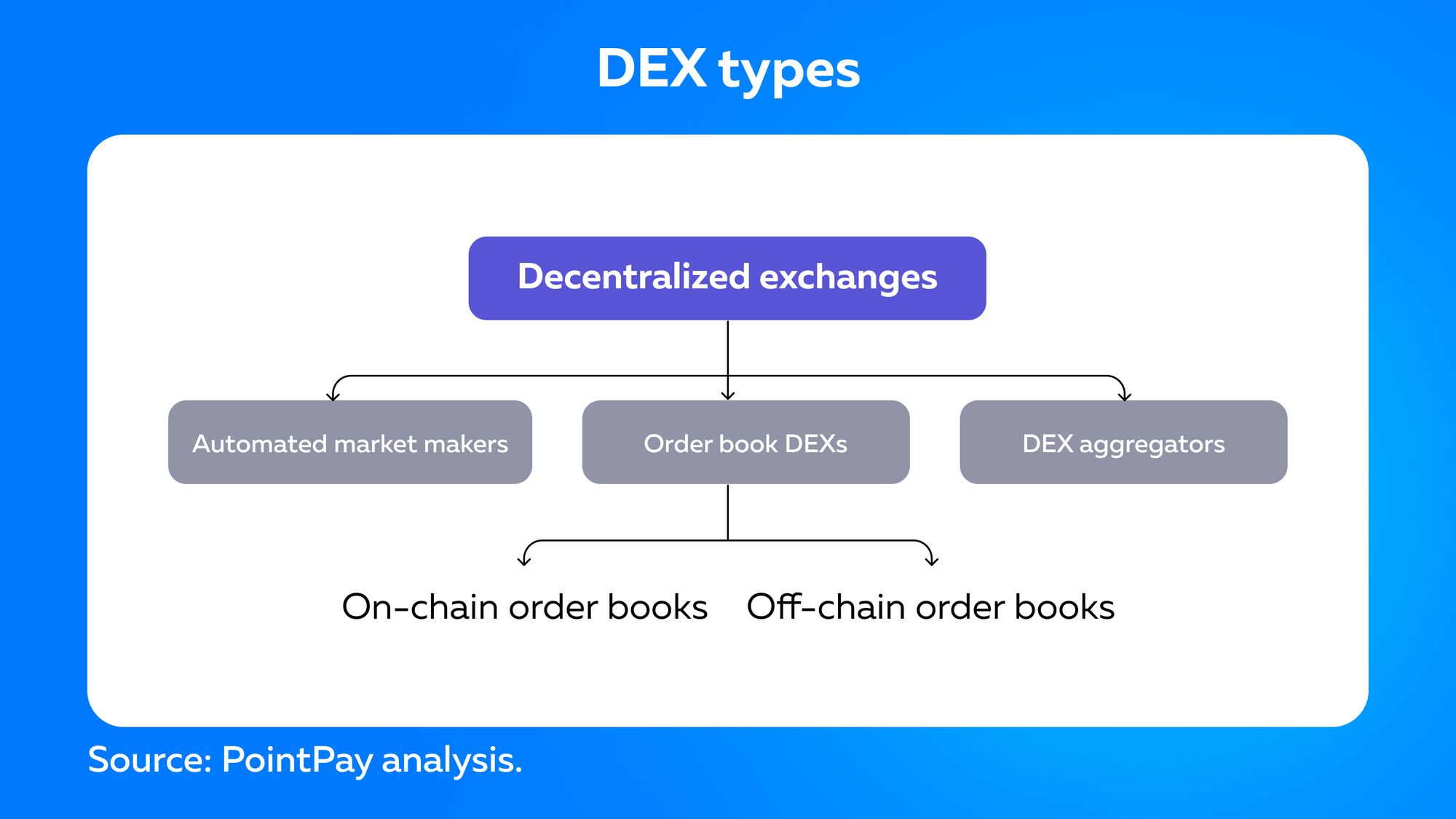
What are the different types of DEXes?
DEXs are built directly on the blockchain. There are three main types of them:
- Automated market makers (AMM);
- Order books DEXs;
- DEX aggregators.
Let’s go over some of the key differences between these types!
Automated Market Makers (AMM)
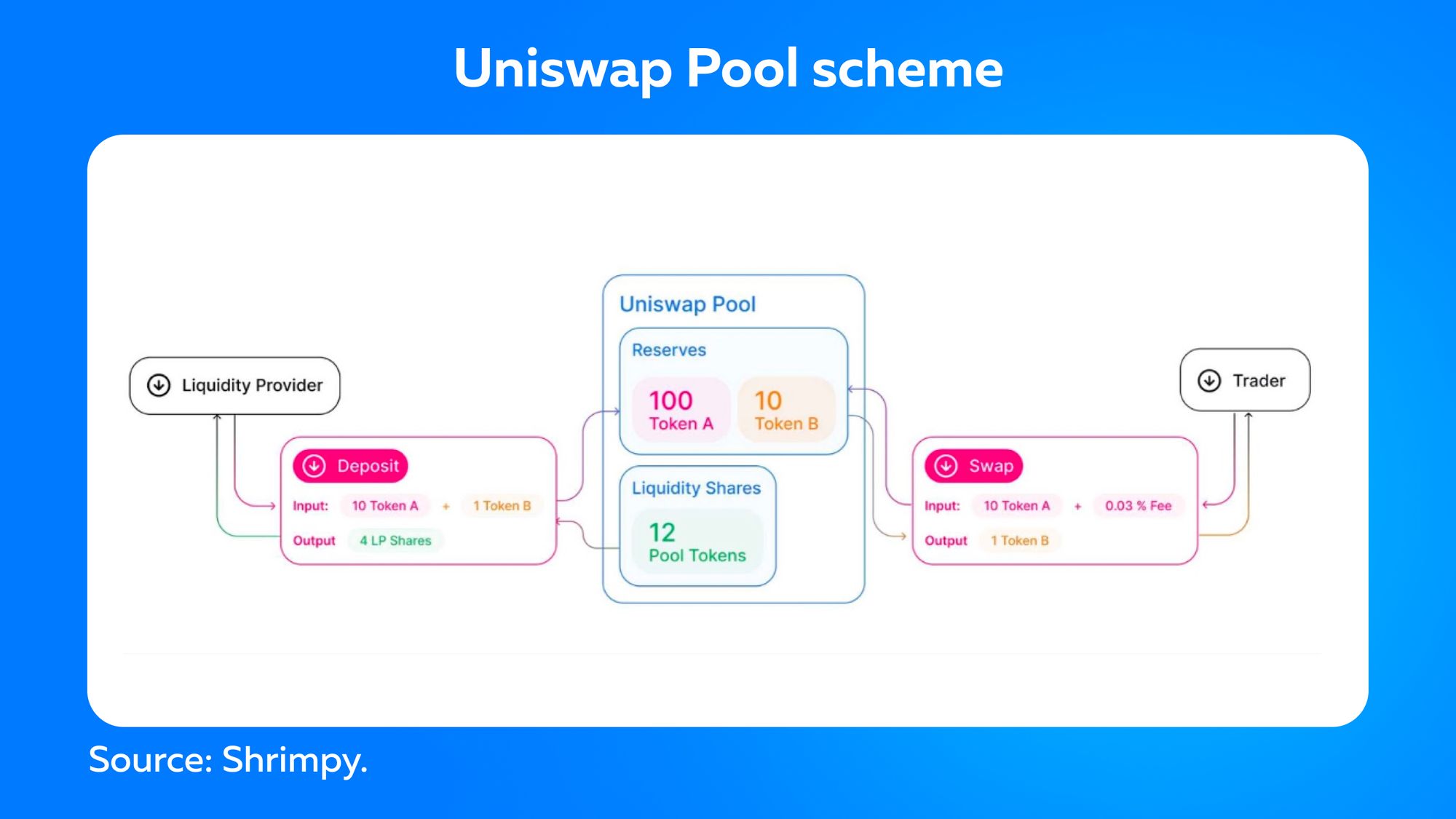
AMM is a protocol used by most DEXes. It was developed to solve the liquidity problem. With AMM, you don't have to wait for a person to meet the price you want to trade. Instead, you trade with a "pool of funds" rather than a person. The pools are funded by other users, who then receive a transaction fee the protocol charges for executing trades on a particular pair.
An AMM algorithm dictates how expensive a particular asset should be based on how much there is. For instance, if someone buys more ETH, it becomes more expensive because there's less of it. If someone sells Ethereum, it becomes cheaper because there's more of it. We can say that it's a simple supply and demand, but a system is used to execute it instead of a person. These AMMs rely on blockchain-based services that provide information from exchanges and other platforms to set the price of traded assets. The three most popular decentralized exchanges using AMM are Uniswap, Curve, and SushiSwap.
Order Book DEXs
Decentralized exchanges initially used the same type of order books as centralized. Order books record all open buy and sell orders for specific pairs of assets. Buy orders indicate that a trader is willing to buy or bid for an asset at a certain price, while sell orders indicate that a trader is ready to sell or ask for a certain price. The spread between these prices determines the depth of the order book and the market price on the exchange.
DEXs that use order books usually keep this information on-chain during trades while your funds remain off-chain in your wallet. However, the DEX platforms that hold their order books off the blockchain only settle trades on the blockchain to bring the benefits of centralized exchanges to traders. Using off-chain order books helps exchanges reduce costs and increase speed to guarantee that trades are executed at the desired price.
DEX Aggregators
DEX aggregators are systems that use several different protocols and mechanisms to solve problems associated with liquidity. Protecting users from the pricing effect and decreasing the likelihood of failed transactions are two other significant goals of DEX aggregators. Some DEX aggregators also use liquidity from centralized platforms to provide a better user experience. By integrating with certain centralized exchanges, they nevertheless don't remain anonymous providers.
Pros and Cons of DEXes
With the popularity of DEX, many improvements have been made to make them more accessible and trustworthy.
Advantages
Reduced security risks
As DEX doesn’t control traders' funds, experienced cryptocurrency users who have custody of their funds are at a reduced risk of being hacked.
Greater Transparency
Another advantage is that DEXs usually offer greater transparency into the liquidity, movement of funds, and trades that take place.
Anonymity
In contrast to centralized exchanges, users do not need to go through a standard identification process known as Know Your Customer (KYC). Many traders like this about DEXs, as their privacy is kept and secured while they trade!
Speed
DEXs are certainly faster, allowing you to trade in counted minutes.
There are many advantages of decentralized exchanges, but some drawbacks are worth discussing.
Disadvantages
Unvetted token listings
Perhaps one of the main issues is that anyone can list a new asset and provide liquidity by pairing it with other coins. If you are not careful enough, you might end up with a scam token.
Hot Storage Device
Compared to CEX, where your token sits on their exchange, you will need to connect your wallet to the internet physically via your computer or connect it with an extension like MetaMask.
Limited Trading Functionality
DEXs tend to focus on executing simple buy and sell orders. Advanced functions such as stop losses, margin trading, and lending are usually not available.
How do you interact with a DEX?
With a decentralized exchange, there is no registration process. You don't even need an email address to interact with these platforms. Instead, traders require a compatible wallet and internet access.
- When using DEXs, the first step is deciding which network to use- each trade will incur a transaction fee.
- The next one is to choose a wallet that's compatible with the selected network and fund it with the native token used to pay for fees. Wallet extensions such as Metamask make it easy to interact with DEXes. They can be installed like any other extension and require users to either import an existing wallet through a seed phrase or private key or create a new one. A password further secures this process.
- Now, you need to buy the tokens used to pay transaction fees on the chosen network through centralized exchanges. Once the user has bought these tokens, they must withdraw them from their wallet to a new one they control.
- Now you can connect your crypto wallet to the DEX platform, usually by clicking the "Connect Wallet" button in the upper corner of the DEX website.
DEXes are constantly evolving
DEXs will certainly hold their place in the crypto ecosystem with the accessibility, ease, transparency, speed of innovation, permissionless, and censorship resistance that they can provide.
Nowadays, decentralized exchanges let users borrow funds to leverage their positions, collect trading fees by providing liquidity, or lend funds to earn interest. As new platforms are built on self-executing smart contracts, more use cases may be created in the future.
Nevertheless, it is hard for platforms to enforce KYC and AML verification. Regulators might try to implement traditional checks on decentralized platforms. Let's take a look at what the future holds for decentralized trading platforms!
🔥 Buy PXP tokens on Bittrex: https://bit.ly/32VWsci
🔥 Buy PXP tokens on Bitrue: https://bit.ly/3JEreHu
🔥 Buy PXP tokens on BitHumb: https://bit.ly/3qOK6e9
🔥 Buy PXP tokens on WhiteBIT: https://bit.ly/3qJrjRH
🔥 Buy PXP tokens on CoinTiger: https://bit.ly/3pnv6ny
💰 Earn up to 7% yearly with PXP staking program in PointPay Bank: https://bank.pointpay.io/staking
💡 Check PointPay Live-Roadmap (PointPay development in real-time): https://pointpay.io/live-roadmap/
🏦 Remember, we are PointPay, and we are beyond banking!