Stagflation refers to a state of the economy in which prices rise while economic activity slows down. The term "stagflation" was proposed by British politician Ian MacLeod in a speech before the House of Commons in 1965, a time of economic stress in the United Kingdom. This phenomenon first entered textbooks in the 1970s, when an oil crisis caused prices to rise, coinciding with a sharp drop in GDP.
In this article, we will examine what stagflation is and what role cryptocurrencies can play in the global economy during this time.
What is stagflation?
Stagflation is an economic phenomenon combining economic stagnation with inflation. Stagflation is characterized by:
- rising inflation;
- a slowdown in economic growth;
- growing unemployment.
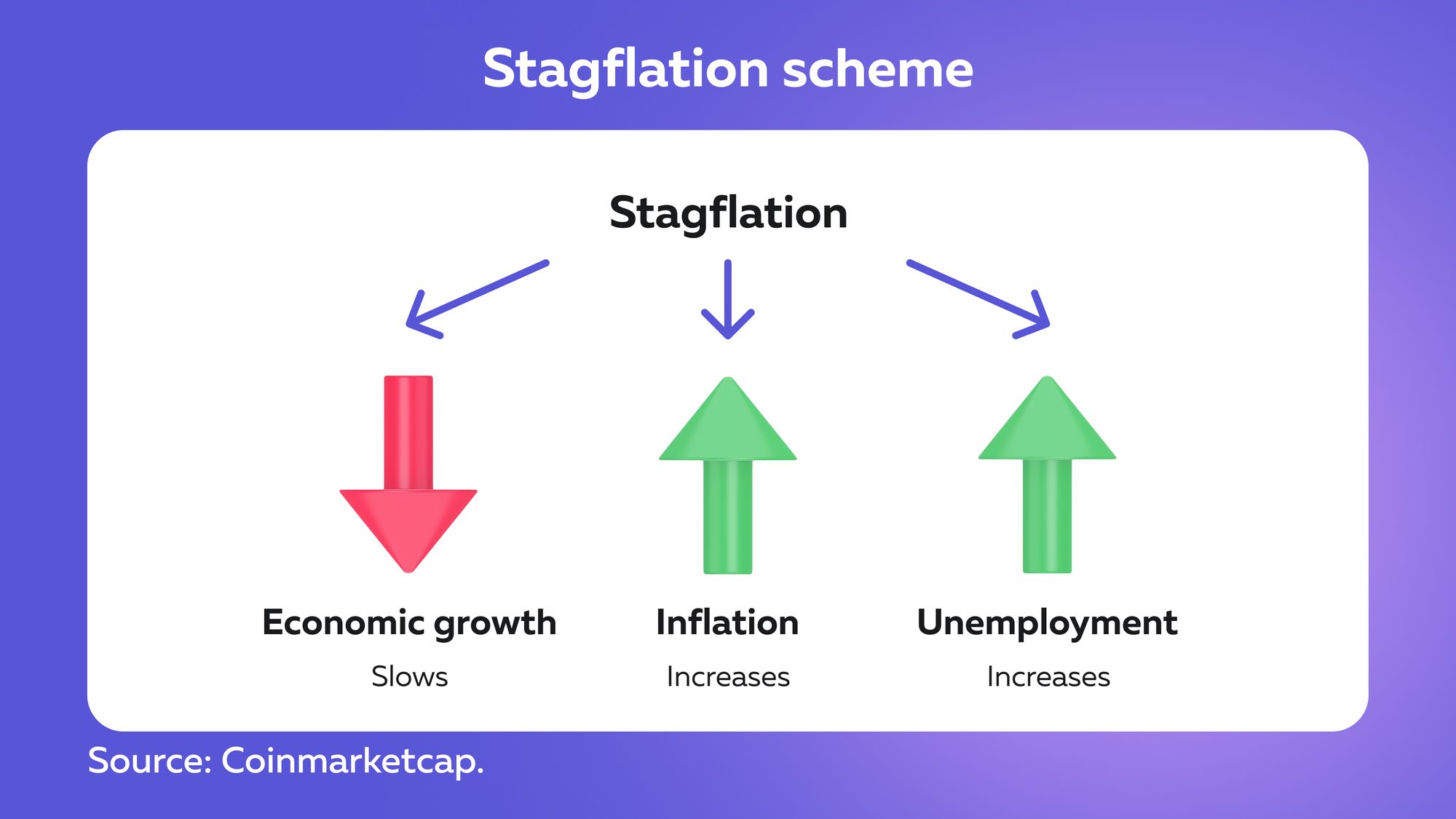
Unfavorable combination: reducing inflation increases unemployment while reducing unemployment will lead to an increase in inflation. In simple terms, inflation is a prolonged rise in the prices of goods and services, but it can also be described as a continuing decline in purchasing power.
The combination of a declining supply and a longer-than-expected duration of the pandemic caused by the Delta coronavirus is holding back the economic recovery. Survey data from the US, UK, and Eurozone show that activity has slowed down due to longer delivery times and accumulation of incomplete orders. A sharp slowdown in production growth was noted in China, where regulatory pressure and high energy prices led to the shutdown of some industries.
Why does stagflation occur?
Economists have different theories about what caused the phenomenon, but there are two main theories:
- Supply shock
It means an unexpected increase or decrease in the supply of a good or service. For instance, a sudden increase in the cost of oil leads to higher prices, increases production costs, and reduces profits.
2. Ineffective economic policy
The government is pursuing policies that hurt industries by increasing the money supply too quickly, leading to a slowdown in production, sales, and higher inflation.
Why is stagflation bad for the economy?
A slowdown in economic growth is a normal part of the macroeconomic cycle. When financial speculation rises (as happened to technology stocks in the late 1990s and the housing market in the mid-2000s), the market needs to stabilize. A recession is a temporary, albeit painful, process that helps stock prices return to their normal levels.
But stagflation has a different cause from inflation: in the former case, a long period of an economic recession is combined with high inflation rates. The process of stagflation can develop in the shortest possible time, as it happened in the 1990s of the twentieth century. At that time, all the negative consequences accumulated like a snowball, but resolving the situation took several years.
The risk of the emergence and development of a crisis manifests itself in the following ways:
- Decrease in GDP compared to previous periods
However, the value of the gross domestic product may fluctuate, but without a significant drop in the country's rating in the general list of world states.
- Noticeable deterioration of the credit system
It is manifested in the growth of rates, a sharp decrease in the total number of loans issued, including a reduction in business support programs from the state.
- Endemic unemployment or its manifestation in a particular sector
This is possible with the mass modernization of production, the transition to automated labor, or other reasons. As a result, the burden on the budget due to benefits paid to the unemployed will increase.
The situation is generally reflected in the well-being of the population of the countries. The demand for goods and services falls significantly without the opportunity to find a job or take out a loan. This partly causes an increase in prices and a decrease in demand for labor.
Is there a cure for stagflation?
The cure for stagflation is not known, but the consensus among economists is that productivity has to increase so that growth without inflation can occur, which would then enable the tightening of monetary policy. This is easier said than done, so the key to preventing stagflation is for economic policymakers to be proactive.
The currency situation
Inflation in major economies is at multi-year highs, such as the United States' 9.1% in June 2022.
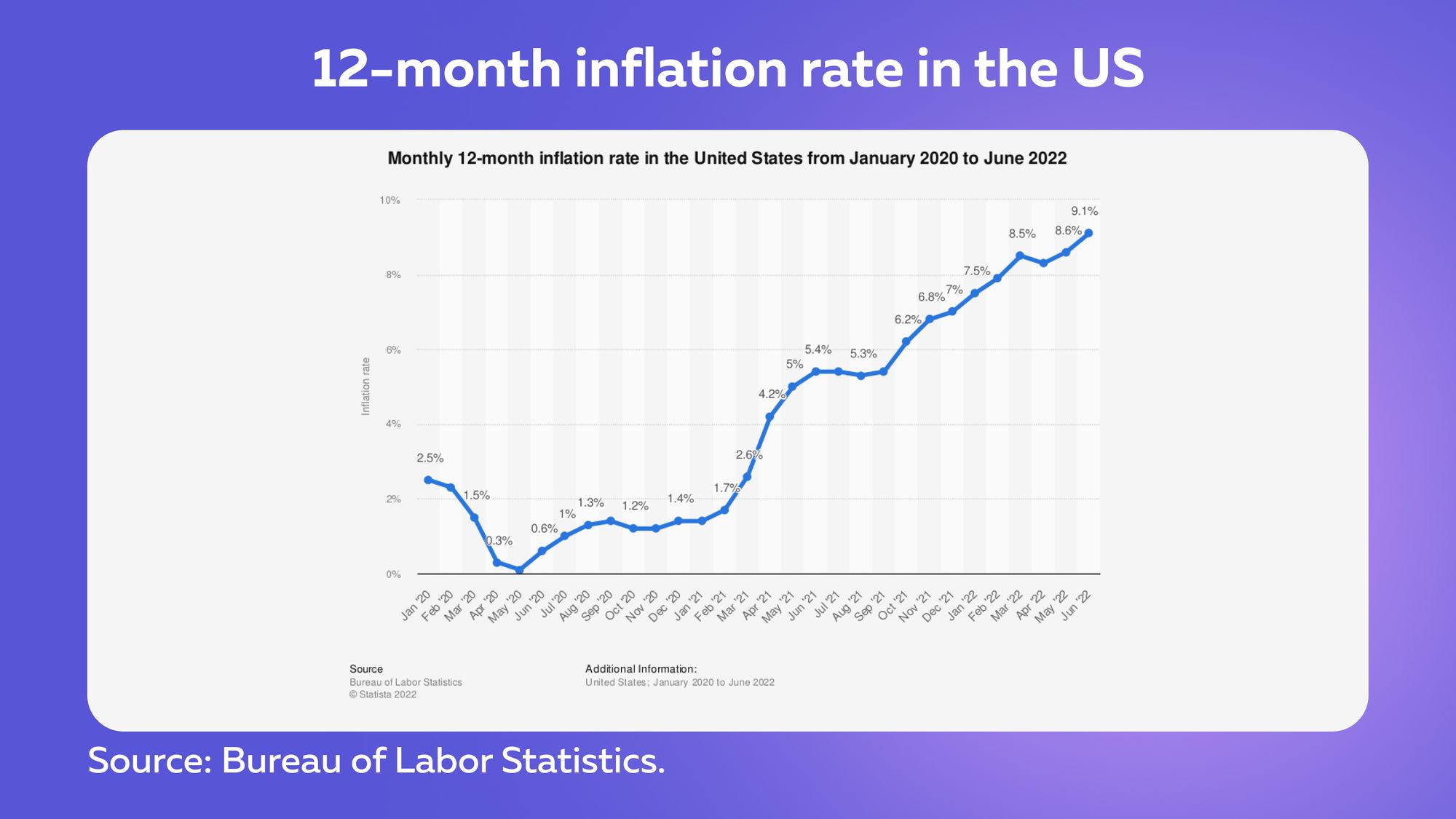
During the covid-19 pandemic, developed countries have implemented easy money strategies to stimulate economic recovery. In March 2020, the interest rates were cut to a range of 0.1% to 0.25% before beginning to raise them last month to the current 0.50%. These rates are expected to be raised in the nearest future.
The US printed over $13 trillion in spending since 2020. It's printing new money to fund debt relief, infrastructure, and economic stimulus programs. This is true for other major economies as well.
Rising prices can reduce people's purchasing power, affecting household budgets and the value of savings. This leads to less disposable income, which decreases aggregate demand in the economy.
When aggregate demand falls, companies' sales revenues fall, and interest rates rise. People in first-world countries are encouraged to save more as interest payments increase. The Federal Reserve Bank of the US, Bank of England, and European Central Bank have already hiked interest rates to control inflation. If banks continue this policy, loans will become expensive, and stock markets will weaken.
What effects does Stagflation have on the Cryptocurrency markets?
The crypto markets tend to mirror stock market sentiment. During periods of stagflation, investors tend to hedge against economic downturns by investing in hard assets such as gold and silver.
Some experts predict that stagflation could catalyze the adoption of Bitcoin and crypto. Both have many of the same properties. Accordingly, investors may consider Bitcoin a useful way to preserve their purchasing power.
Moreover, some economists believe that stagflation could cause the crypto markets to decouple from equity markets. In particular, if marginal gains decline further in the stock markets, crypto could seem a viable alternative.
Bitcoin's supply held by exchanges is the most powerful factor, increasing the likelihood of Bitcoin decoupling from equities. A recent CoinDesk article reports the amount of Bitcoin held by exchanges fell 18% in April 2022 compared to May 2020. As balance continues to shrink, low Bitcoin liquidity may cause the price to become more volatile, resulting in decoupling.
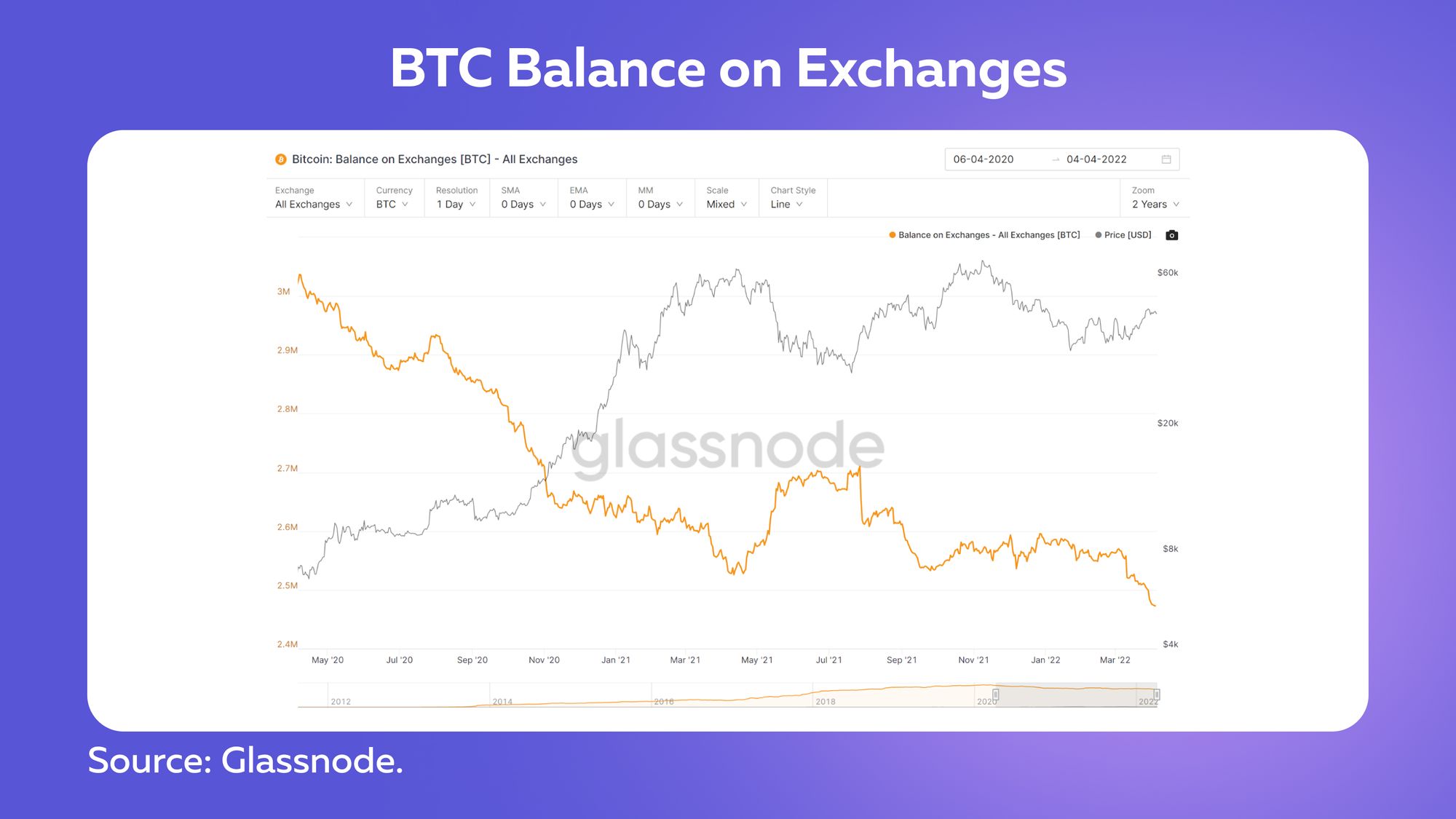
Bitcoin's decoupling from equities could indicate that widespread adoption of the leading cryptocurrency is accelerating. This could be the fundamental underlying factor driving the global adoption of digital assets.
PointPay is a platform that brings all your assets under one roof, allowing you to control them easily and conveniently. Our product has brought the best of traditional financial services and the benefits of modern technologies together. And it's making a difference around the world.